9 person circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle is a tough one to solve in assured steps
The tough 9 person circular seating reasoning puzzle for SBI PO solved quickly in easy steps by primary barrier identification and effective logic analysis.
Circular seating reasoning puzzles are inherently confusing, and with 9 persons, the present circular seating puzzle is understandably a hard one to solve.
This demand more time to analyze all condition together, identify the primary barrier and select the most promising condition statement that would give us maximum gains.
Strategic and tactical selection of logic condition statements at each stage as well as compact representation of the logic table will play important part in successful solution of such high level reasoning puzzles in quick time.
For more knowledge and practice you may refer to the list of tutorials and solved reasoning puzzles given at the end.
High level 9 person Circular seating Reasoning Puzzle for SBI PO
Problem description
Nine people namely Bree, Cini, Epu, Fiji, Gyan, Hal, Lipi, Monu and Rani sit around a circular table. Four of them face away from the center, and the rest face towards the center. Each of them likes to travel to a different type of place among, Hill, Forest, Temple, Beach, City, Heritage, Desert, Lake and River but not necessarily in the same order.
The following is what we know about them.
Conditional statements
- Rani is second to the left of Lipi who doesn't like to travel to places of types Heritage, Desert, Hill.
- Monu likes to travel to Lake.
- The one who likes to travel to Temple is fourth to the right of the one who likes Forest.
- The person who likes Forest is facing away from the center.
- Lipi is fourth to the right of Hal, whose facing direction is same as that of Cini.
- Cini, who likes City, is sitting fifth to the left of Fiji, who is an immediate neighbor of Rani.
- Gyan does not like Hill, Heritage or Desert type of place.
- Epu likes Heritage travel.
- The one who likes Desert is facing towards the center as Gyan faces but they are not neighbors of each other.
- Desert travel is not liked by Rani.
- Hal is facing away from the center.
- Hill travel is not liked by Hal.
- The one who likes Beach is sitting second to the right of the one who likes Hill.
- Cini is second to the left of Bree who likes Forest.
- Rani is in the group of Gyan in terms of facing direction.
- Monu is facing away from the center and is second to the right of Epu.
- Temple travel is liked by a person who is facing away from the center.
Questions
Question 1. Who is sitting second to the right of Bree?
- Monu
- Cini
- Rani
- Gyan
- Fiji
Question 2. The person on the second right of Lipi likes to travel to,
- Desert
- Hill
- River
- Beach
- Lake
Question 3. Which of the following combinations is correct?
- Fiji-Hill-Facing away
- Bree-Forest-Facing in
- Rani-Lake-Facing away
- Epu-Heritage-Facing in
- Hal-Desert-Facing away
Question 4. Whose neighbor on the right among the following face away from the center?
- Rani
- Cini
- Hal
- Fiji
- Gyan
Question 5. Who among the following is an immediate neighbor of the one who likes Heritage?
- The one who likes Temple
- The one who likes Forest
- Hal
- Both 1 and 3
- Fiji
Question 6. Who among the following sits third to left of the person who likes Lake?
- The one who likes Hill
- Cini
- Bree
- Epu
- The one who likes Desert
Solution to the 9 person Circular seating arrangement Reasoning Puzzle for SBI PO
Logic table representation
After going through all the logic conditions briefly, we form our conclusions based on initial problem analysis:
- The number of persons 9 and number of logic conditions 17, both are large.
- A few conditions directly state facing direction thus helping quick solution. We have to identify and use these early in the process.
- A number of position separation conditions exist for resolving position assignment to persons, but majority of these are constrained by absence of facing direction and so are not immediately usable. We have to know the facing directions first.
- A critical given information is, number of facing away directions is 4. This is the key to solving the problem. Our main objective will then be to find the facing directions of all or most of the persons at the earliest. Finding facing direction is the main barrier and first we will resolve this barrier using limitation of facing away directions. This is primary barrier identification.
- Overall, by the nature of condition statements, the problem is not as difficult as it seems.
The following logic table will be used for solving the problem.
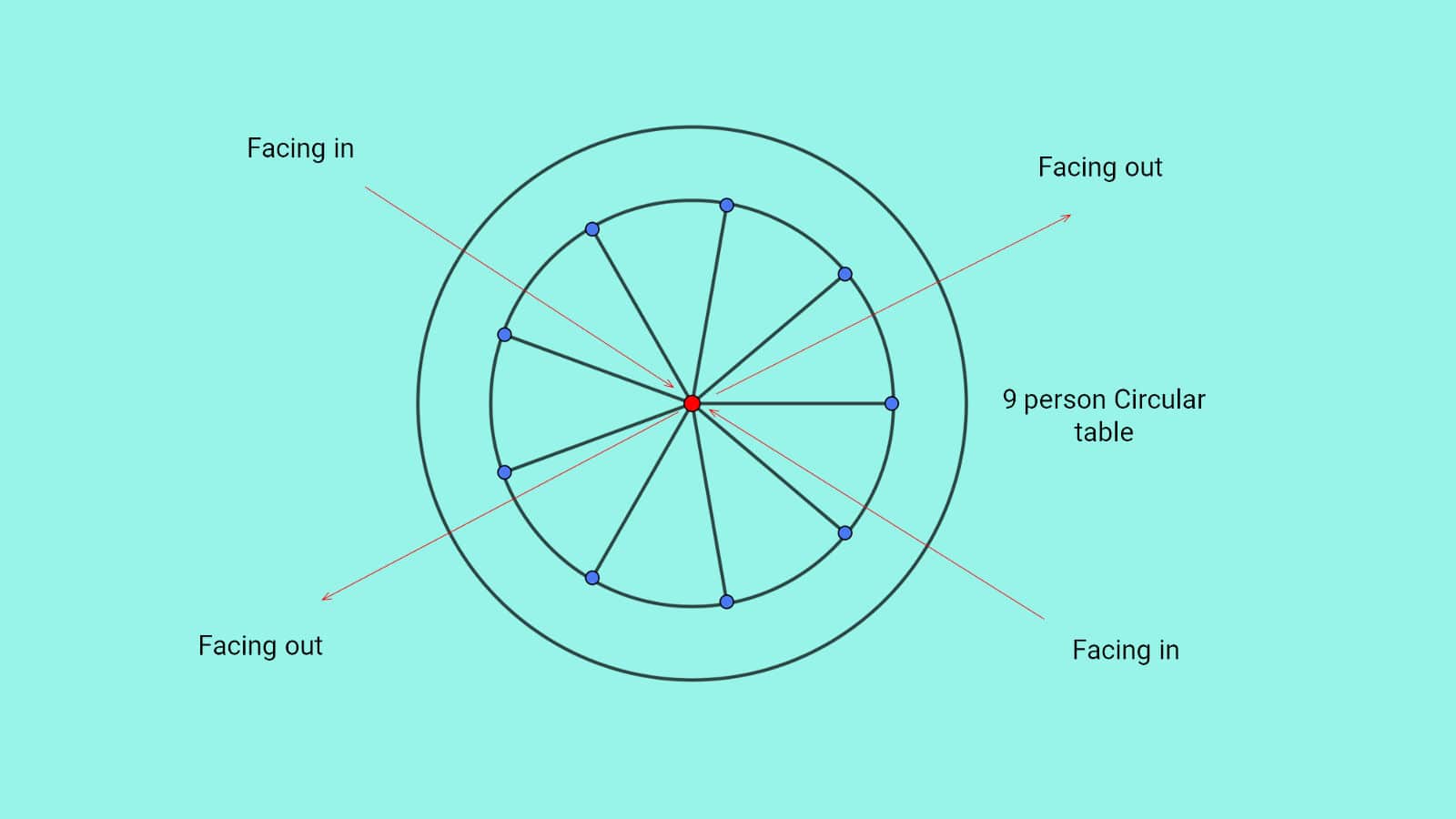
Nine logic table positions correspond to nine positions in the round table with the implicit understanding that the two end positions 1 and 9 are adjacent, and the logic table loops back to simulate a round table.
Facing value "I" means facing towards center and "O" means facing away from center. Depending on the facing direction, the left or right direction of the person sitting at a position will be determined.
In first row, persons will be assigned or seated at the positions, and the second row will have the travel place the person sitting at the position likes. Third row values will indicate the facing direction of the person sitting in the specific position.
Relative positions in a round table
In a round table, as no position has specific significance to any END (a round table has no END), relative positions of the persons sitting on such a table are only important, the position numbers are not. This is why when we place a person first on the empty table positions, we have the freedom to place the person at any position. But after this first placement, the freedom is no longer there. All further placements are constrained and are relative to the first placement and later individual placements. During this intermediate phase of placement, the position numbers become essential for specific reference.
After we are able to complete all assignments, the table won't have any empty cell.
Solution to 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO Stage 1: First condition selection and further condition analysis
With our main objective of determining facing directions as quickly as possible, the first condition selection and maximum certain assignment of persons to positions is of prime importance at the start.
General guideline for first condition candidate is, select first the statement that will enable you to make direct and certain assignments to the maximum extent.
Note: without knowing the facing direction of a person, we can't make a certain first assignment.
Statement 4, Statement 9, Statement 11 and Statement 17 each makes direct assignment of at least two parameters, but using Link search technique on "Forest" we identify Statement 4 and Statement 14 which together fix the position of person liking forest facing away, as well as fix the relative position of Cini. Together we select these two as the best candidates for first condition processing with maximum amount of direct certain assignment with ease (no less than four parameters are assigned). We call this strategy of selecting one or more than one statement with maximum capacity for direct certain assignment as direct assignment strategy.
As all cells are equivalent at the start in a circular seating representation, at the first assignment we have the freedom to place the fixed relation first assignments at any position of the logic table. We have this freedom only on the first move. Later placements will be relative to this first assignment.
In this problem then we select Statement 4 first and Statement 14 next as the first group of statements to be processed.
Additionally, to speed up our solution, we search for link term or common term in these two statements and find in Statement 3 link term "Forest" mentioned, resulting in another direct assignment. Continuing link search further with respect to the Statement 3, we find Statement 17 in which the term "Temple" is mentioned linking these two statements and results in away facing direction for person liking Temple travel. Thus we process all the four statements together at first stage to achieve a good amount of certainty in assignment at the very first stage, a total of 6 assignments.
Statement 4. The person who likes Forest is facing away from the center.
Statement 14. Cini is second to the left of Bree who likes Forest.
Statement 3. The one who likes to travel to Temple is fourth to the right of the one who likes Forest.
Statement 17. Temple travel is liked by a person who is facing away from the center.
The status at this first stage is shown below.

Now we will concentrate on statements that refer directly or indirectly to facing away directions.
Solution to 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO Stage 2: Finding facing directions and using temporary work area
Among the rest of the statements, Statement 16 directly defines facing away direction of Monu but as we are unable to process its second part referring Epu's unknown direction, we record this information by appending statement number 16 in brackets with Monu. This assignment does not refer to any fixed position and we use it for the sole purpose of determining who faces which direction. The information is recorded below the main logic table in temporary work area.
Similarly we record facing away direction for Hal in temporary work area from Statement 11.
Following our general strategy, after reaching a certain stage, we always search for a promising new statement linked by a common term. Using this link search technique next we identify the Statement 5 in which Hal is referred to in relation to Lipi. This last statements form fixed position of Lipi relative to Hal to create what we call a bonded structure or position separated fixed structure. As we are not yet able to assign these persons with certainty on any position of the table, these relatively positioned bonded persons are recorded in the temporary work area. With this Statement 5, as a bonus, we get the facing away direction of Cini. It is a double reference information rich statement executed at the very right time.
At this second stage, we process these three statements one after the other.
Statement 16. Monu is facing away from the center and is second to the right of Epu; (We hold back second part for later reference and use only the first part now).
Statement 11. Hal is facing away from the center.
Statement 5. Lipi is fourth to the right of Hal, whose facing direction is same as that of Cini.
We will first show the result of processing these three statements in sequence in the logic table and then will explain the results and consequences.
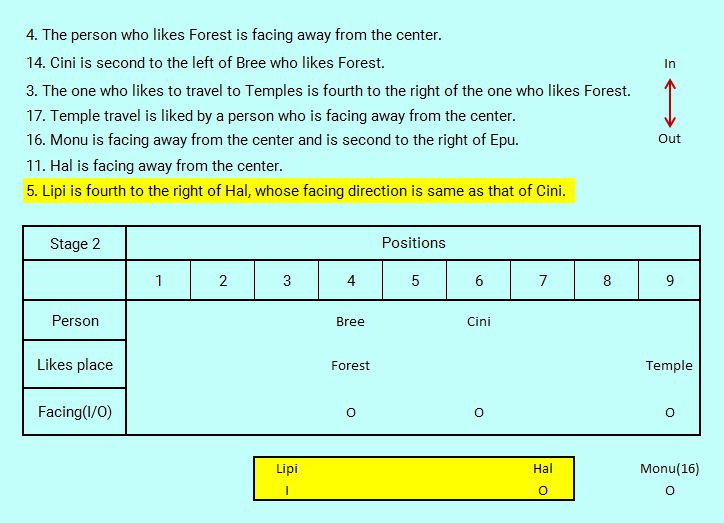
In the Lipi--Hal combination, the positions with respect to each other are fixed even though we can't place these two persons on the table with certainty. That's why this bonded structure is recorded in the temporary work area below the main table.
Breakthrough in determining facing directions
From the logic table we find five numbers of facing away directions (value "O"), and as positions of Monu and Hal are still uncertain, one of the two has to occupy the position 9 with Temple liking and facing away direction to make the total number of facing away direction as 4. There is no doubt about that.
From this, we can draw a second and third certain conclusions that,
- no person other than these four with facing away direction can be sitting in facing away direction, and so,
- all the rest, that is, Lipi, Rani, Gyan, Fiji and Epu must be facing the center of table (with code value "I").
This series of reasoning is Elementary logic analysis which form the backbone of any logic analysis.
So we have achieved our breakthrough in determining facing directions of all persons.
With this knowledge, all the statements with positional relations will hopefully point to fixed position assignments.
Solution to 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO Stage 3: Preparing to place the bonded structures onto the table positions
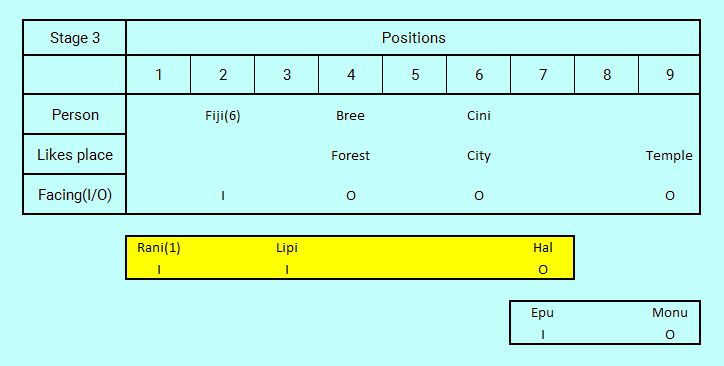
At this stage we would process the ignored part of the Statement 16. "Monu is facing away from the center and is second to the right of Epu." first. As we now know Epu to face in, we can form a fixed two-member bonded structure with Monu second to the right of Epu.
Now searching for additional referenced links we identify Statement 1 that refers to Rani in relation to Lipi. Execution of this statement places Rani second left of Lipi who is facing in.
Statement 1. Rani is second to the left of Lipi who doesn't like to travel to places of types Heritage, Desert, Hill.
The second part of Statement 1 we just record in a bracket with Rani as "Rani(1)" to be processed when more travel place details are available. Rani expands Hal's bonded structure to a three-member bond.
The Statement 5 is highlighted because it provided the critical breakthrough to overcome the barrier of facing directions.
We have now two bonded structures in the temporary work area. Before further analysis, following link search we find Statement 6 that refers to Fiji in relation to Cini and results another certain assignment of Fiji who occupies position 2 with certainty. As a bonus we get travel liking of Cini as City. Second part of Statement 6 is kept on hold (though we won't need it finally for making any decisions, it is superfluous information).
Statement 6. Cini, who likes Cities, is sitting fifth to the left of Fiji, who is an immediate neighbor of Rani.
Let us show again the logic table and its temporary area results with these small changes at the third stage.
Solution 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO Stage 4: Placing all persons onto certain positions
We will now try to place bonded structures: "Rani--Lipi--Hal" and: "Epu--Monu" onto the logic table without any conflict in positions.
There are only two possible options for placing Hal, position 7 and position 9. But if we place Hal in position 7, we won't be able to place the other two-member bond of Epu--Monu in any position. This provides conflict which is frequently used in this way for certain placements.
On the other hand, if we place Hal in position 9 (with Lipi in position 5 and Rani in position 3), Epu goes to position 8 and Monu to position 1 without any problem because of rounded table property of logic table looping back. So this is the last breakthrough of positioning persons. After placing these five persons, we place Gyan, the last remaining person to position 7, the last remaining vacant position. This is what we call Principle of exclusion.
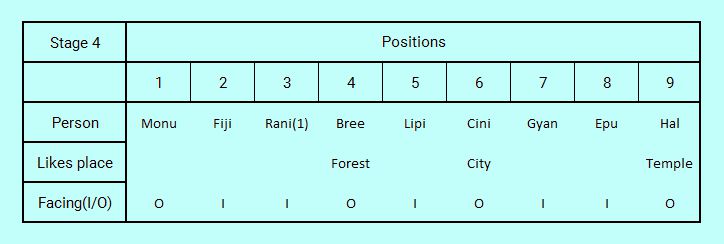
Solution to 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO Stage 5: Placing travel places to complete assignments
Main hurdles crossed, we will now select Statement 8 and Statement 2 as both assigns travel liking directly.
Statement 8. Epu likes Heritage travel.
Statement 2. Monu likes to travel to Lake.
Now only we bring the second part of Statement 1. "Lipi doesn't like Heritage, Desert, Hill" into action and find only Beach or River left for Lipi.
Statement 13 generates two possibilities for Hill--Beach combination (all the to be assigned positions are now inward facing), either Hill with Rani or Lipi. But as Lipi doesn't like Hill, Rani gets Hill and Lipi Beach satisfying second part of Statement 1 and Statement 13. With Desert and River left, with Statement 7, as Gyan doesn't like Hill, Heritage or Desert, Gyan gets the remaining place type River and Fiji gets Desert. Assignments over, all places filled up.
Statement 13. The one who likes Beach is sitting second to the right of the one who likes Hill.
Statement 7. Gyan does not like Hill, Heritage or Desert type of place.
The final solved logic table is shown below.
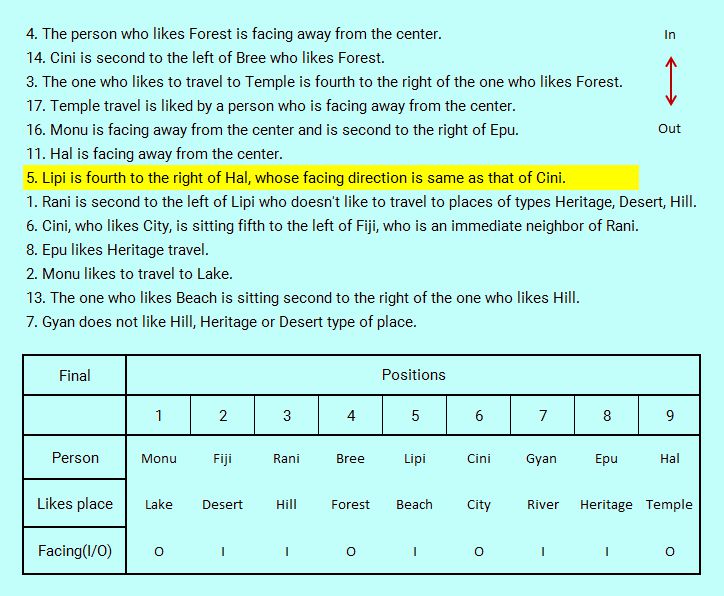
Now we are ready to answer the six given questions and it should take only about a minute's time to answer.
Answers to the questions: 9 person Circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzle for SBI PO
Question 1. Who is sitting second to the right of Bree?
Answer 1. Option 5: Fiji.
Question 2. The person on the second right of Lipi likes to travel to,
Answer 2. Option 3: River.
Question 3. Which of the following combinations is correct?
Answer 3. Option 4: Epu-Heritage-Facing in.
Question 4. Whose neighbor on the right among the following face away from the center?
Answer 4. Option 1: Rani.
Question 5. Who among the following is an immediate neighbor of the one who likes Heritage?
Answer 5. Option 4: Both 1 and 3.
Question 6. Who among the following sits third to left of the person who likes Lake?
Answer 6. Option 3. Bree.
Takeaways
Overall analysis and main barrier identification: From initial analysis of all conditions, main barrier identified as finding four facing away directions at the earliest.
Start of puzzle problem solving: Selection of first condition to process. In this case, to speed up the process, link search applied to identify as many as four conditions that resulted in 6 assignments at the first stage.
Directed logic analysis: With main objective in view, all the facing away directions assigned as far as possible. In doing so, at a crucial statement, by elementary logic analysis barrier of finding facing direction broken through and facing directions of all persons assigned with certainty. After knowing facing directions focus shifted to forming position linked bonded member structures to resolve positions of all persons. This has been the second goal after the first was met. Lastly once the positions of persons ascertained goal changed to identifying all travel liking by selecting directly referenced travel liking first.
General logic analysis strategies: Higher information content more valuable statement. General direct assignment strategy for selection of first condition to process, Continuing link search with common term reference as long as possible so that certain assignments are increased as much as possible at one go before the next stage of analysis.
Frequently used and highly effective specific logic analysis techniques: Direct assignment strategy, Link search technique, Conflict analysis, Principle of exclusion, Bonded structure formation and expansion. For efficiency, bonded structures are recorded in temporary work area as well as unprocessed part of a condition recorded with the assigned member for later processing.
Promising positional relations between members: fixed positional separation arrangement or bonded structure.
Condition statement value: Potential certain assignments by direct reference or chain linking references. Promising positional relations. Statements referring to larger number of parameters in positive context contain higher amount of positive information and so are more valuable.
Comment
The compact representation of logic table is important, but critical is the ability to choose the most effective sequence of executing the logic statements. That is possible only by a well-developed strategy based logic analysis methodology.
To be comfortable with such puzzle solving of any structure and type, there is no alternative other than solving many problems of various types and always analyzing how the puzzle was solved, and learn.
Superfluous conditional statements
As many as four statements were left untouched being not needed for final assignments. These were superfluous, though these were used for verification of the final assignment. In a way this reflects the efficiency and speed of the solution process.
Analytical approach examples
The whole solution process consists of a number of examples of analytical approach.
End note
Solving reasoning puzzles does not need knowledge on any subject—it is just identifying useful patterns by analysis of the problem and using appropriate methods. It improves problem solving skill, because patterns and methods lie at the heart of any problem solving.
Other resources for learning how to discover useful patterns and solve logic analysis problems
Einstein's puzzle or Einstein's riddle
The puzzle popularly known as Einstein's puzzle or Einstein's riddle is a six object set assignment logic analysis problem. Going through the problem and its efficient solution using collapsed column logic analysis technique in the session Method based solution of Einstein's logic analysis puzzle whose fish should be a good learning experience.
Playing Sudoku
As a powerful method of enhancing useful pattern identification and logic analysis skill, play Sudoku in a controlled manner. But beware, this great learning game, popularly called Rubik's Cube of 21st Century, is addictive.
To learn how to play Sudoku, you may refer to our Sudoku pages starting from the very beginning and proceeding to hard level games.
Reading list on SBI PO and Other Bank PO level Reasoning puzzles
Tutorials
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 1
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 2
How to solve SBI PO level family relation problems in a few simple steps 3
How to solve SBI PO level floor stay Reasoning Puzzle in a few confident steps 4
How to solve high level circular seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 5
How to solve high level hard two row seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 6
How to solve high level circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzles for SBI PO quickly 7
How to solve high level circular seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO quickly 8
How to solve high level box positioning reasoning puzzle for SBI PO quickly 9
Solved reasoning puzzles SBI PO type
SBI PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 1
SBI PO type high level reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 2
SBI PO type high level reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 3
SBI PO type high level circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 4
SBI PO type high level hard reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 5
SBI PO type high level one to many valued group based reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 6
SBI PO type high level hard two in one circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 7
SBI PO type hard facing away circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 8
SBI PO type high level four dimensional reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 9
SBI PO type hard two row seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 10
SBI PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 11
Solved Reasoning puzzles of Bank PO type
Bank PO type two row hybrid reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 1
Bank PO type four variable basic assignment reasoning puzzle solved in a few steps 2
Bank PO type basic floor based reasoning puzzle solved in a few steps 3
Bank PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in quick steps 4
