A four dimensional reasoning puzzle to test assignment logic analysis skills
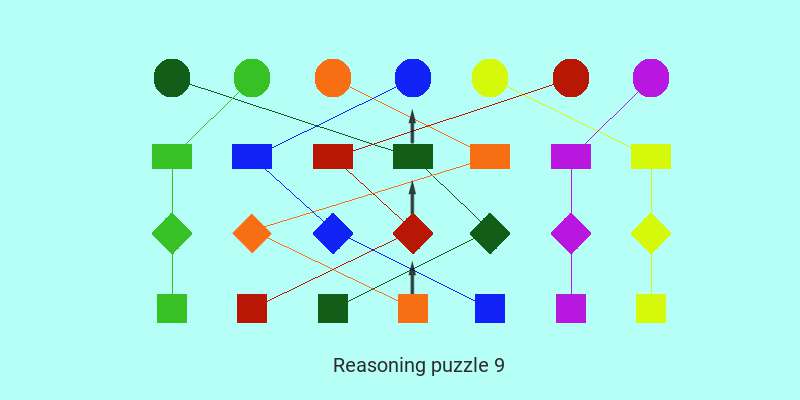
In this ninth session on solving a SBI PO type high level reasoning puzzle in a few easy and confident steps without confusion, the puzzle chosen is again a pure assignment type logic analysis problem involving four object sets that are to be assigned to each other on one to one basis. The logic state representation being simple for such problems, the core element of logic analysis skill gains prime importance.
For detailed concepts on the fundamental techniques and strategies used in solving this type of logic puzzles you should refer to our tutorial sessions,
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 1
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 2
How to solve SBI PO level family relation problems in a few simple steps 3
How to solve SBI PO level floor stay Reasoning Puzzle in a few confident steps 4
How to solve high level circular seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 5
How to solve high level hard two row seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 6
Note: Before going through the solution of the problem, try to solve the problem in a suitably timed exercise session.
SBI PO type high level Reasoning Puzzle with four object sets: Who has which profession, is from which place and likes which color?
Problem description
There are seven persons Rio, Mani, Chiku, Kuttu, Priya, Anik and Sanju with one of them from Pune. Each of them is from a different place, has a different profession, and likes a different color.
Conditional statements
- Chiku, a judge, is from Kota.
- Priya and Anik like green and magenta, though not necessarily in that order.
- Rio is not from Kulu.
- The person from Kulu is a writer and likes blue.
- The reporter likes yellow.
- The politician from Puri likes magenta.
- The professor and the musician like violet and red, though not necessarily in that order.
- Anik is a logician.
- The person from Raipur is a professor.
- The person from Delhi likes red.
- Sanju from Jammu does not like pink.
- Mani is a musician.
Questions
Question 1. Who likes color Blue?
- Kuttu
- Anik
- Chiku
- Sanju
- Rio
Question 2. What is the place of the logician?
- Delhi
- Kota
- Puri
- Jammu
- Pune
Question 3. What is the color that the person from Raipur likes?
- Red
- Violet
- Magenta
- Pink
- Green
Question 4. What is the color that Anik likes?
- Red
- Magenta
- Yellow
- Green
- Pink
Question 5. Which of the following combinations is correct?
- Puri-Red
- Chiku-Kulu
- Judge-Pink
- Delhi-Reporter
- Rio-Musician
Note: Try to solve the problem yourself before going through the solution.
Solution to the SBI PO type high level hard reasoning puzzle with four object sets: Problem analysis and representation
The number of object sets is a healthy 4, the 7 persons, their 7 places, their 7 professions and 7 colors they like. Assignments between the members of the object sets is to be done on one to one basis.
Two specialties are observed:
- Except the names of the persons, the names of the other three sets are not given explicitly beforehand in the problem description. These names appear in the logic conditions gradually.
- Secondly, the number of logic statements is 12, a fairly large number that should attract careful attention in dealing with the set of conditions.
The names of the persons form the primary object set representing the column labels, as all the other three object sets are attributes of the persons. The places, professions and the liked colors form three simple rows.
Primary focus will be on selectng the right statement at the right time. In other words, the strategic logic condition analysis will be of prime importance in solving this problem. If approached randomly, this puzzle may prove to be quite confusing.
The logic table representation we will work on is as follows.
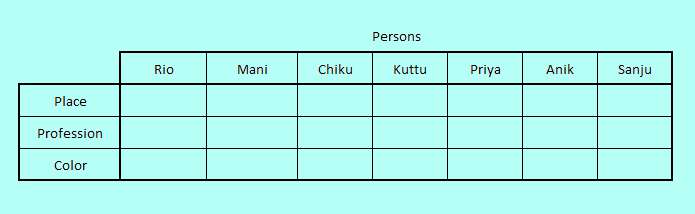
This is the first problem in our series of puzzle solving sessions where we are not able to note the set member lists on top of the logic table for keeping track of which member is yet to be assigned. We have to keep track of left out members on an ongoing basis.
Solution Stage 1: Direct assignments with no uncertainty first, followed by two degree uncertainty
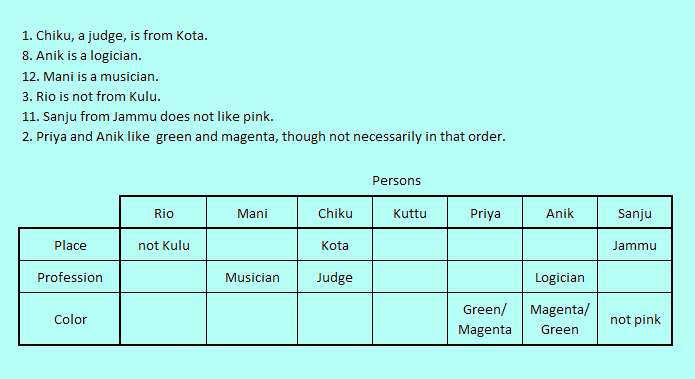
We will first execute the statement that makes maximum number of direct certain assignments. Statement 1. "Chiku, a judge, is from Kota." is chosen first as it makes two certain assignments which is the maximum compared to the other statements. We put Kota and Judge against place and profession rows and Chiku column.
In the same vein, the next statements executed are, Statement 8. "Anik is a logician." and Statement 12. "Mani is a musician." as both are certain assignments of degree 1 with no uncertainty. We avoid dealing with statements involving uncertainties in the beginning.
Statement 3. "Rio is not from Kulu." allows us to record a 7 degree uncertainty "not Kulu" against the Rio column. This uncertainty should be resolved much later and it is not mixing up things in any way. So we accept its uncertainty.
Next we execute degree 1 certainty Statement 11. "Sanju from Jammu does not like pink." and write just "not Pink" against the color row of Sanju column.
Next we choose Statement 2. "Priya and Anik like green and magenta, though not necessarily in that order." with two degree uncertainty. This type of statement is also very useful because it blocks two values of an object set between two cells. No other celll can have those values which are as good as assigned.
We write both values as "Green/ Magenta" and "Magenta/ Green" against the two cells. When any one of these cells gets a certainty later, that value is cancelled and by uncertainty cancellation, the other cell also gets the second value with certainty. This is the hallmark of two degree uncertainties.
The logic table after this stage is as below,
Solution Stage 2: Strategy 2: Link search technique, conflict, and uncertainty cancellation as well as exclusion
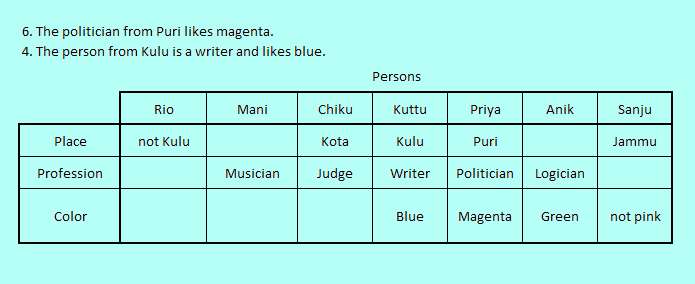
Now we identify a reference to Magenta in Statement 6. "The politician from Puri likes magenta." which because of conflict in profession for Anik fixes Magenta-Puri-Politician triplet to Priya. Consequently we get Green for Anik by uncertainty cancellation.
The only other triple valued Statement 4. "The person from Kulu is a writer and likes blue." has no other column left except Kuttu. resulting in a 3 valued certain assignment.
The logic table now looks like,
Solution Stage 3: Strategy 3: Conflict results in a certain assignment and we record a two degree uncertainty
Now with the logic table fairly populated it is time to locate statements that produce certain assignments by conflict. The Statement 9. "The person from Raipur is a professor." creates two conflicts in profession Professor at place in vacant columns Mani and Anik, leaving a single certain possibility at Rio column.
Before closing this stage we decide to record an acceptable two degree uncertainty (which is usually very useful) by Statement 7. "The professor and the musician like violet and red, though not necessarily in that order." putting both the color values Violet and Red in the corresponding two cells.
The logic table at this stage is as shown below.
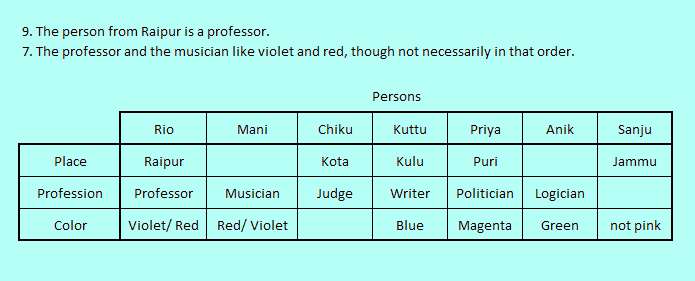
Out of the two statements left we would choose Statement 10. "The person from Delhi likes red." as it resolves the two degree uncertainty just introduced. Red and Delhi gets Mani by conflict at Rio. So Red goes to Mani and by uncertainty cancellation, Violet goes to Rio.
Last Statement 5. "The reporter likes yellow." puts Reporter to only vacant profession of Sanju who also gets color Yellow. By exclusion Pink goes to Chiku and Pune to Anik.
All statements are exhausted in assigning the logic table fully and thus we classify this puzzle as a well-formed assignment logic analysis puzzle without any superfluous statement.
The final logic table state is as below,
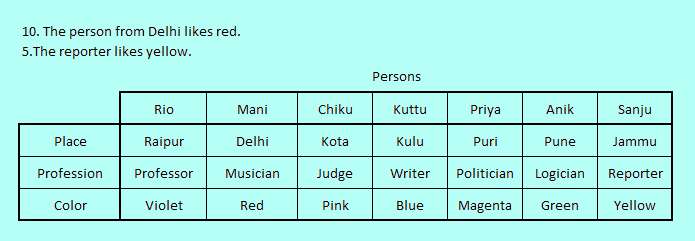
Now we are ready to answer the questions and it should take only about a minute's time to answer the five questions.
Answers to the questions
Question 1. Who likes color Blue?
Answer 1. Option 1: Kuttu.
Question 2. What is the place of the logician?
Answer 2. Option 5: Pune.
Question 3. What is the color that the person from Raipur likes?
Answer 3. Option 2: Violet.
Question 4. What is the color that Anik likes?
Answer 4. Option 4: Green.
Question 5. Which of the following combinations is correct?
Answer 5. Option 3: Judge-Pink.
Recommendation
You need to carefully go through these sessions for absorbing the concepts well, and more importantly you must solve a number of such problems of various types for solving such a problem or its variation in the actual test confidently.
End note
Solving reasoning puzzles does not need knowledge on any subject—it is just identifying useful patterns by analysis of the problem and using appropriate methods. It improves problem solving skill, because patterns and methods lie at the heart of any problem solving.
Other resources for learning how to discover useful patterns and solve logic analysis problems
Einstein's puzzle or Einstein's riddle
The puzzle popularly known as Einstein's puzzle or Einstein's riddle is a six object set assignment logic analysis problem. Going through the problem and its efficient solution using collapsed column logic analysis technique in the session Method based solution of Einstein's logic analysis puzzle whose fish should be a good learning experience.
Playing Sudoku
As a powerful method of enhancing useful pattern identification and logic analysis skill, play Sudoku in a controlled manner. But beware, this great learning game, popularly called Rubik's Cube of 21st Century, is addictive.
To learn how to play Sudoku, you may refer to our Sudoku pages starting from the very beginning and proceeding to hard level games.
Reading list on SBI PO and Other Bank PO level Reasoning puzzles
Tutorials
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 1
How to solve SBI PO level logic puzzles in a few simple steps 2
How to solve SBI PO level family relation problems in a few simple steps 3
How to solve SBI PO level floor stay Reasoning Puzzle in a few confident steps 4
How to solve high level circular seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 5
How to solve high level hard two row seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO in confident steps 6
How to solve high level circular seating arrangement reasoning puzzles for SBI PO quickly 7
How to solve high level nine position circular seating reasoning puzzles for SBI PO quickly 8
How to solve high level box positioning reasoning puzzle for SBI PO quickly 9
Solved reasoning puzzles SBI PO type
SBI PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 1
SBI PO type high level reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 2
SBI PO type high level reasoning puzzle solved in a few confident steps 3
SBI PO type high level circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 4
SBI PO type high level hard reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 5
SBI PO type high level one to many valued group based reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 6
SBI PO type high level hard two in one circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 7
SBI PO type hard facing away circular seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 8
SBI PO type high level four dimensional reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 9
SBI PO type hard two row seating reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 10
SBI PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 11
Solved reasoning puzzles Bank PO type
Bank PO type two row hybrid reasoning puzzle solved in confident steps 1
Bank PO type four variable basic assignment reasoning puzzle solved in a few steps 2
Bank PO type basic floor based reasoning puzzle solved in a few steps 3
Bank PO type high level floor stay reasoning puzzle solved in quick steps 4
